Functions | |
| int | current_umask () |
| List[str] | split_leading_dir (str path) |
| bool | has_leading_dir (Iterable[str] paths) |
| bool | is_within_directory (str directory, str target) |
| None | set_extracted_file_to_default_mode_plus_executable (str path) |
| bool | zip_item_is_executable (ZipInfo info) |
| None | unzip_file (str filename, str location, bool flatten=True) |
| None | untar_file (str filename, str location) |
| None | unpack_file (str filename, str location, Optional[str] content_type=None) |
Variables | |
| logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) | |
| SUPPORTED_EXTENSIONS = ZIP_EXTENSIONS + TAR_EXTENSIONS | |
Detailed Description
Utilities related archives.
Function Documentation
◆ current_umask()
| int current_umask | ( | ) |
Get the current umask which involves having to set it temporarily.
Definition at line 43 of file unpacking.py.
References i.
Referenced by pip._internal.utils.unpacking.set_extracted_file_to_default_mode_plus_executable().
◆ has_leading_dir()
| bool has_leading_dir | ( | Iterable[str] | paths | ) |
Returns true if all the paths have the same leading path name (i.e., everything is in one subdirectory in an archive)
Definition at line 62 of file unpacking.py.
References pip._internal.utils.unpacking.split_leading_dir().
Referenced by pip._internal.utils.unpacking.untar_file(), and pip._internal.utils.unpacking.unzip_file().
◆ is_within_directory()
| bool is_within_directory | ( | str | directory, |
| str | target | ||
| ) |
Return true if the absolute path of target is within the directory
Definition at line 77 of file unpacking.py.
References i.
◆ set_extracted_file_to_default_mode_plus_executable()
| None set_extracted_file_to_default_mode_plus_executable | ( | str | path | ) |
Make file present at path have execute for user/group/world (chmod +x) is no-op on windows per python docs
Definition at line 88 of file unpacking.py.
References pip._internal.utils.unpacking.current_umask(), and i.
◆ split_leading_dir()
| List[str] split_leading_dir | ( | str | path | ) |
Definition at line 50 of file unpacking.py.
References i.
Referenced by pip._internal.utils.unpacking.has_leading_dir(), pip._internal.utils.unpacking.untar_file(), and pip._internal.utils.unpacking.unzip_file().
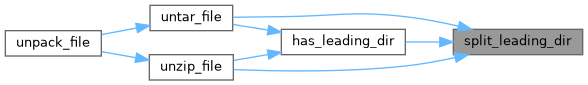
◆ unpack_file()
Definition at line 229 of file unpacking.py.
References i, pip._internal.utils.unpacking.untar_file(), and pip._internal.utils.unpacking.unzip_file().
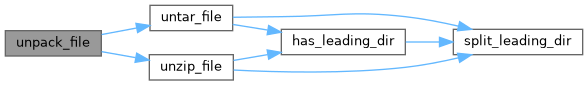
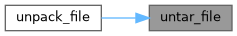
◆ untar_file()
| None untar_file | ( | str | filename, |
| str | location | ||
| ) |
Untar the file (with path `filename`) to the destination `location`. All files are written based on system defaults and umask (i.e. permissions are not preserved), except that regular file members with any execute permissions (user, group, or world) have "chmod +x" applied after being written. Note that for windows, any execute changes using os.chmod are no-ops per the python docs.
Definition at line 149 of file unpacking.py.
References pip._internal.utils.unpacking.has_leading_dir(), i, and pip._internal.utils.unpacking.split_leading_dir().
Referenced by pip._internal.utils.unpacking.unpack_file().

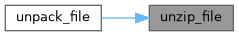
◆ unzip_file()
| None unzip_file | ( | str | filename, |
| str | location, | ||
| bool | flatten = True |
||
| ) |
Unzip the file (with path `filename`) to the destination `location`. All files are written based on system defaults and umask (i.e. permissions are not preserved), except that regular file members with any execute permissions (user, group, or world) have "chmod +x" applied after being written. Note that for windows, any execute changes using os.chmod are no-ops per the python docs.
Definition at line 103 of file unpacking.py.
References pip._internal.utils.unpacking.has_leading_dir(), i, and pip._internal.utils.unpacking.split_leading_dir().
Referenced by pip._internal.utils.unpacking.unpack_file().

◆ zip_item_is_executable()
| bool zip_item_is_executable | ( | ZipInfo | info | ) |
Definition at line 96 of file unpacking.py.
References i.
Variable Documentation
◆ logger
| logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) |
Definition at line 22 of file unpacking.py.
◆ SUPPORTED_EXTENSIONS
| SUPPORTED_EXTENSIONS = ZIP_EXTENSIONS + TAR_EXTENSIONS |
Definition at line 25 of file unpacking.py.